Detecting the onset of accelerated long-term forgetting: evidence from temporal lobe epilepsy
Article
McGibbon, Terence and Jansari, A. 2012. Detecting the onset of accelerated long-term forgetting: evidence from temporal lobe epilepsy. Neuropsychologia. 51 (1), pp. 114-122.
| Authors | McGibbon, Terence and Jansari, A. |
|---|---|
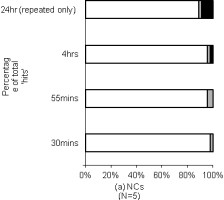
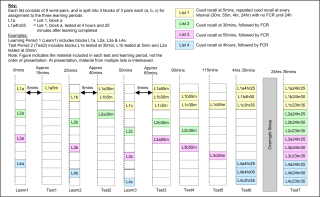
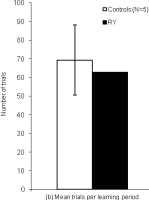
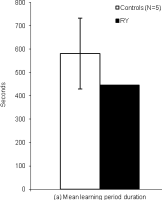
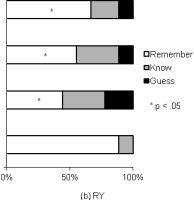
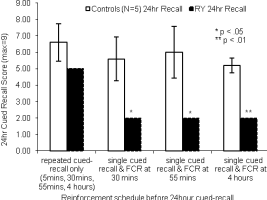
| Abstract | Accelerated long-term forgetting (ALF) refers to a slowly developing anterograde amnesia in which material is retained normally over short delays but then forgotten at an abnormally fast rate over days to weeks. Such long-term memory impairment is not detected by standard clinical tests. This study analysed ALF in a temporal lobe epileptic, RY. Key issues addressed were: (i) the timeframe of ALF onset; (ii) whether disruption of memory consolidation during sleep is a necessary requirement for precipitating ALF; (iii) the effectiveness of repeated recall in limiting the impact of ALF. RY's memory for novel word-pairings was compared with that of matched controls using cued-recall and forced choice recognition (FCR) tests at multiple delays (5, 30, 55, 240 min). To investigate the impact of repeated recall some pairings were recalled at all intervals, and all material (repeatedly and non-repeatedly recalled) was tested again after a 24 h delay. RY's initial learning and performance at 30 min were normal, but by 55 min both his cued-recall performance and the subjective quality of his recognition memory were significantly impaired. This suggests disruption of secondary consolidation processes occurring relatively soon after learning. It also raises the possibility of developing a standard test to diagnose ALF within a single clinical session rather than requiring multiple visits. Since RY remained awake it appears that disruption of memory consolidation during sleep is not a necessary condition for him to experience ALF. Repeated recall at multiple time-points within the first 4 h sustained normal recall performance to 24 h, indicating repeated recall could form the basis for a protective strategy. |
| Keywords | Accelerated long-term forgetting (ALF); Temporal lobe epilepsy; Long-term amnesia (LTA) |
| Journal | Neuropsychologia |
| Journal citation | 51 (1), pp. 114-122 |
| ISSN | 0028-3932 |
| Year | 2012 |
| Publisher | Elsevier |
| Accepted author manuscript | |
| Web address (URL) | http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2012.11.004 |
| Publication dates | |
| 19 Nov 2012 | |
| Publication process dates | |
| Deposited | 27 Nov 2012 |
| Copyright information | NOTICE: this is the author’s version of a work that was accepted for publication in Neuropsychologia. Changes resulting from the publishing process, such as peer review, editing, corrections, structural formatting, and other quality control mechanisms may not be reflected in this document. Changes may have been made to this work since it was submitted for publication. A definitive version will be published in Neuropsychologia at http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S002839321200471X |
| File | |
| File | |
| File | |
| File | |
| File | |
| File | |
| File |
https://repository.uel.ac.uk/item/85y56
Download files
367
total views801
total downloads7
views this month10
downloads this month