Salvinorin A content in legal high products of Salvia divinorum sold in Mexico
Article
Hernández-Bello, Rafael, García-Rodríguez, Rosa Virginia, García-Sosa, Karlina, Peña-Rodríguez, Luis Manuel, Vázquez-Hernández, Maribel, Ramos-Morales, Fernando Rafael, Corcoran, O. and Alberto, Sánchez-Medina 2015. Salvinorin A content in legal high products of Salvia divinorum sold in Mexico. Forensic Science International. 249 (April), pp. 197-201. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.forsciint.2015.01.038
| Authors | Hernández-Bello, Rafael, García-Rodríguez, Rosa Virginia, García-Sosa, Karlina, Peña-Rodríguez, Luis Manuel, Vázquez-Hernández, Maribel, Ramos-Morales, Fernando Rafael, Corcoran, O. and Alberto, Sánchez-Medina |
|---|---|
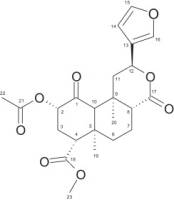
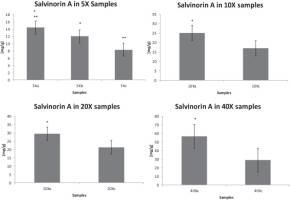
| Abstract | Salvia divinorum (Lamiaceae) is a herb native to Mexico where is used by Mazatec shamans for spiritual and divination purposes. S. divinorum products are easily available to consumers and are used worldwide as legal highs because of the hallucinogenic effects caused mainly by salvinorin A. Highly popular videos and websites in the internet depicting the use of S. divinorum products have contributed to an increase in their consumption. Recent reports have highlighted the potential of these products to induce psychosis in consumers. In Mexico, dried leaf extracts of S. divinorum are sold in different strengths, claiming to correlate with increasing amounts of salvinorin A. In order to determine the variability of salvinorin A content between brands and to investigate possible correlation between brand strengths, this study sought to quantify salvinorin A in commercial products available in Mexico using an HPLC method. The HPLC analytical method showed a correlation coefficient R2 > 0.99, with LOD of 0.44 μg/mL and LOQ of 1.34 μg/mL. The retention time for salvinorin A was 23.09 ± 0.95 min and the measured concentrations ranged between 8.32 ± 0.65 to 56.52 ± 3.77 mg/g dried leaf. The results for brand c did not show an agreement between the declared and the calculated amount of salvinorin A. Additionally, the emergence in Mexico of high strength salvia products (100x), the lack of regulation and the observed variability of salvinorin A content between brands of commercial legal highs products of S. divinorum could result in a health problem for consumers. |
| Keywords | Legal highs; HPLC method; Salvia divinorum; salvinorin A |
| Journal | Forensic Science International |
| Journal citation | 249 (April), pp. 197-201 |
| ISSN | 03790738 |
| Year | 2015 |
| Publisher | Elsevier |
| Accepted author manuscript | License CC BY |
| Accepted author manuscript | License CC BY |
| Accepted author manuscript | License CC BY |
| Accepted author manuscript | License CC BY |
| Accepted author manuscript | License CC BY |
| Accepted author manuscript | License CC BY |
| Digital Object Identifier (DOI) | https://doi.org/10.1016/j.forsciint.2015.01.038 |
| Publication dates | |
| 07 Feb 2015 | |
| Publication process dates | |
| Deposited | 16 Feb 2015 |
| Accepted | 26 Jan 2015 |
| Funder | Consejo Nacional de Ciencia y Tecnología de México |
| Universidad Veracruzana | |
| Consejo Nacional de Ciencia y Tecnología | |
| Universidad Veracruzana |
https://repository.uel.ac.uk/item/85735
Download files
Accepted author manuscript
| 1-s2.0-S0379073815000523-main.pdf | ||
| License: CC BY | ||
 | table(3).csv | |
| License: CC BY | ||
 | table(4).csv | |
| License: CC BY | ||
 | table(5).csv | |
| License: CC BY | ||
| 1-s2.0-S0379073815000523-gr1.jpg | ||
| License: CC BY | ||
| 1-s2.0-S0379073815000523-gr2.jpg | ||
| License: CC BY | ||
2848
total views2866
total downloads3
views this month10
downloads this month
Export as
Related outputs
Prebiotics may alter bile salt hydrolase activity: Possible implications for cholesterol metabolism
Adebola, O., Corcoran, O. and Morgan, W. 2020. Prebiotics may alter bile salt hydrolase activity: Possible implications for cholesterol metabolism. PharmaNutrition. 12 (Art. 100182). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phanu.2020.100182G-protein αq gene expression plays a role in alcohol tolerance in Drosophila melanogaster
Aleyakpo, B., Umukoro, O., Kavlie, R., Ranson, D., Thompsett, A., Corcoran, O. and Casalotti, S. 2019. G-protein αq gene expression plays a role in alcohol tolerance in Drosophila melanogaster. Brain and Neuroscience Advances. 3. https://doi.org/10.1177/2398212819883081From Scutellaria barbata to BZL101 in Cancer Patients: Phytochemistry, Pharmacology, and Clinical Evidence
Gao, J., Yin, W. and Corcoran, O. 2019. From Scutellaria barbata to BZL101 in Cancer Patients: Phytochemistry, Pharmacology, and Clinical Evidence. Natural Product Communications. 14 (10). https://doi.org/10.1177/1934578X19880645The Role of Oestrogen Receptor Beta (ERβ) in the Aetiology and Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Ofosu, W. A., Mohamed, D., Corcoran, O. and Ojo, O. 2019. The Role of Oestrogen Receptor Beta (ERβ) in the Aetiology and Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Current Diabetes Reviews. 15 (2), pp. 100-104. https://doi.org/10.2174/1573399814666180119141836Pharmacological targeting of the GABAʙ receptor alters Drosophila's behavioural responses to alcohol
Ranson, D., Ayoub, S., Corcoran, O. and Casalotti, S. 2019. Pharmacological targeting of the GABAʙ receptor alters Drosophila's behavioural responses to alcohol. Addiction Biology. 25 (Art. e12725). https://doi.org/10.1111/adb.12725Pharmacological Modulation of Alcohol Tolerance via GABA-B receptors in Drosophila melanogaster
Ranson, D., Ayoub, S., Corcoran, O. and Casalotti, S. 2018. Pharmacological Modulation of Alcohol Tolerance via GABA-B receptors in Drosophila melanogaster. 11th FENS Forum of Neuroscience. Berlin, Germany 07 - 11 Jul 2018Naltrexone Reverses Ethanol Preference and Protein Kinase C Activation in Drosophila melanogaster
Koyyada, Rajeswari, Latchooman, Nilesh, Jonaitis, Julius, Ayoub, S., Corcoran, O. and Casalotti, S. 2018. Naltrexone Reverses Ethanol Preference and Protein Kinase C Activation in Drosophila melanogaster. Frontiers in Physiology. 9 (175), pp. 1-7. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2018.00175